本文一部分来自于qwen,一部分来自于以下文章:
《CompletableFuture原理与实践-外卖商家端API的异步化》
Java
演进本质
graph LR
A[Java 5 Future] -->|阻塞痛点| B[Guava ListenableFuture]
B -->|回调地狱| C[CompletableFuture]
C -->|流处理需求| D[RxJava]
D -->|Spring整合| E[Reactor]
A -->|范式转变| F[命令式->声明式]
B -->|抽象提升| G[事件驱动->数据流]
C -->|能力增强| H[组合->背压]
D & E -->|统一理念| I[异步即数据流]
控制流:阻塞等待 → 回调响应 → 声明式组合 → 响应式流
错误处理:分散try-catch → 回调onFailure → 链式exceptionally → 流式onError
组合能力:无 → 有限transform → 丰富组合操作符 → 完整流处理
背压支持:无 → 无 → 有限 → 完整内建支持
模式
核心特征
编程范式
适用场景
Java 5 Future
阻塞等待
命令式
简单异步任务,兼容性要求高
Guava ListenableFuture
回调驱动
事件驱动
中等复杂度,需要非阻塞回调
CompletableFuture
链式组合
声明式
复杂异步流程,需要组合和错误处理
RxJava
响应式流
函数式响应式
事件流处理,背压支持,复杂数据转换
Reactor
响应式流
函数式响应式
Spring生态,高性能流处理,背压内建
传统调用时序
Java 5 Future
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#FFF5E1', 'edgeLabelBackground':'#FFF', 'fontFamily': 'monospace'}}}%%
sequenceDiagram
participant Client as Client
participant Executor as ThreadPoolExecutor
participant FutureTask as FutureTask
participant Worker as WorkerThread
Note over Client,Worker: Java 5 Future (阻塞式)
Client->>Executor: submit(Callable)
Executor->>FutureTask: 创建FutureTask
Executor->>Worker: 提交任务
Client->>FutureTask: future.get()
Note right of Client: 阻塞等待结果
Worker->>FutureTask: 执行call()
FutureTask-->>Client: 返回结果
Note over Client: 阻塞调用: future.get()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2 );1000 ); return "Hello Future" ;try {String result = future.get(2 , TimeUnit.SECONDS);catch (TimeoutException e) {"超时了!" );finally {
Guava ListenableFuture
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#D5E8D4', 'edgeLabelBackground':'#FFF', 'fontFamily': 'monospace'}}}%%
sequenceDiagram
participant Client as Client
participant Executor as ListeningExecutorService
participant ListenableFuture as ListenableFuture
participant Worker as WorkerThread
participant Callback as FutureCallback
Note over Client,Callback: Guava ListenableFuture (回调式)
Client->>Executor: submit(Callable)
Executor->>ListenableFuture: 创建ListenableFuture
Executor->>Worker: 提交任务
Client->>ListenableFuture: addCallback(Callback, executor)
Note right of Client: 非阻塞注册回调
Worker->>ListenableFuture: 执行call()
alt 执行成功
ListenableFuture->>Callback: onSuccess(result)
Callback-->>Client: 处理结果
else 执行失败
ListenableFuture->>Callback: onFailure(throwable)
Callback-->>Client: 处理异常
end
Note over Client: 回调模式: onSuccess/onFailure1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 ListeningExecutorService executor = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(2 )1000 );return "Hello ListenableFuture" ;new FutureCallback <String>() {@Override public void onSuccess (String result) {"成功: " + result);@Override public void onFailure (Throwable t) {"失败: " + t.getMessage());
这个方案是很容易产生回调地狱的,因为总是会有 addCallback + onSuccess 这种不可编排、组合 api 不适合把大型并发结果组合在一起的缺陷:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 new FutureCallback <User>() {@Override public void onSuccess (User user) {new FutureCallback <List<Order>>() {@Override public void onSuccess (List<Order> orders) {new FutureCallback <Report>() {@Override public void onSuccess (Report report) {@Override public void onFailure (Throwable t) {"Report generation failed" , t);"report" , t);@Override public void onFailure (Throwable t) {"Order retrieval failed" , t);"orders" , t);@Override public void onFailure (Throwable t) {"User retrieval failed" , t);"user" , t);
CompletableFuture
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#DAE8FC', 'edgeLabelBackground':'#FFF', 'fontFamily': 'monospace'}}}%%
sequenceDiagram
participant Client as Client
participant CF as CompletableFuture
participant Executor as Executor
participant Stage1 as Stage1
participant Stage2 as Stage2
participant Stage3 as Stage3
Note over Client,Stage3: Java 8+ CompletableFuture (声明式)
Client->>CF: supplyAsync(() -> getA(), executor)
CF-->>Stage1: 注册Stage1
Stage1->>CF: thenCompose(a -> getBAsync(a))
CF-->>Stage2: 注册Stage2
Stage2->>CF: thenCombine(getCAsync(), (b,c) -> merge(b,c))
CF-->>Stage3: 注册Stage3
Stage3->>CF: exceptionally(ex -> handle(ex))
CF-->>Client: 返回CompletableFuture
Note right of Client: 非阻塞链式调用
par 异步执行
Executor->>Stage1: 执行Stage1
Executor->>Stage2: 执行Stage2(依赖Stage1结果)
Executor->>Stage3: 执行Stage3(合并结果)
end
CF-->>Client: complete(result)
Client->>CF: thenAccept(result -> process(result))
Note over Client: 链式调用: thenCompose/thenCombineListenableFuture 的改进
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 new FutureCallback <T>() {void onSuccess (T result) ; void onFailure (Throwable t) ;
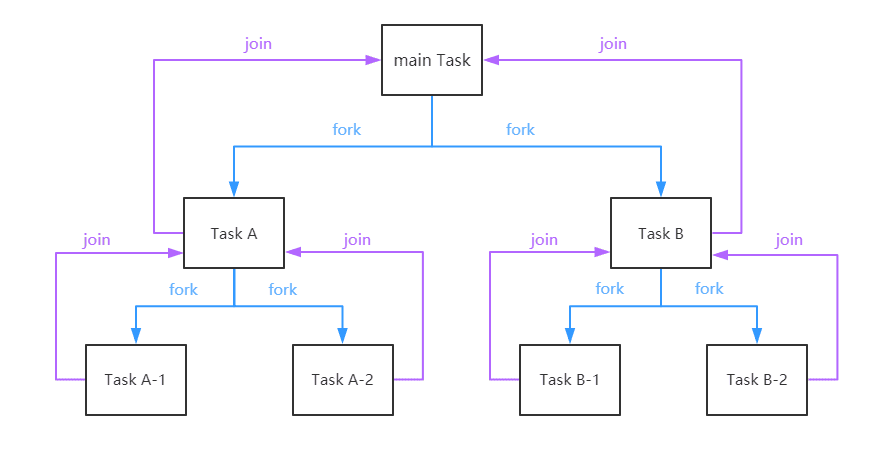
执行树
使用CompletableFuture也是构建依赖树的过程。一个CompletableFuture的完成会触发另外一系列依赖它的CompletableFuture的执行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 import java.util.*;import java.util.concurrent.*;import java.util.stream.Collectors;import java.util.stream.IntStream;public class CompletableFutureThreadContext {public static void main (String[] args) {ExecutorService ioExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20 , new NamedThreadFactory ("io-pool" ));ExecutorService cpuExecutor = new ForkJoinPool (null ,false try {"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 🏃♂️ 主线程开始执行" );0 , 30 )return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] ⚡ 执行服务调用: " + i);return callExternalService(i); "[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 🛡️ 服务[" + i + "]异常处理" );return createServiceFallback(i, ex);2 , TimeUnit.SECONDS);new CompletableFuture [0 ]))5 , TimeUnit.SECONDS)"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 🧮 聚合结果(CPU密集型)" );return serviceFutures.stream()"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 🌐 全局异常处理" );return Arrays.asList(createGlobalFallback(ex));"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] ⏳ 等待最终结果..." );"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] ✅ 最终结果: " + "个成功" );finally {private static ServiceResponse callExternalService (int id) {try {100 + (id % 10 ) * 20 );if (id == 15 || id == 25 ) {throw new RuntimeException ("服务[" + id + "] 模拟故障" );return new ServiceResponse ("Result-" + id, false );catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException ("服务调用被中断" , e);private static ServiceResponse createServiceFallback (int id, Throwable ex) {return new ServiceResponse ("Fallback-" + id, true );private static ServiceResponse createTimeoutFallback (int id) {return new ServiceResponse ("Timeout-" + id, true );private static ServiceResponse createGlobalFallback (Throwable ex) {return new ServiceResponse ("Global-Fallback: " + ex.getMessage(), true );private static void shutdownExecutor (ExecutorService executor) {try {if (!executor.awaitTermination(3 , TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {catch (InterruptedException e) {static class NamedThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {private final String namePrefix;private final AtomicInteger threadNum = new AtomicInteger (1 );this .namePrefix = namePrefix;@Override public Thread newThread (Runnable r) {Thread t = new Thread (r, namePrefix + "-worker-" + threadNum.getAndIncrement());false );"❌ 线程 " + thread.getName() + " 未捕获异常: " + ex.getMessage()));return t;static class ServiceResponse {final String content;final boolean isFallback;boolean isFallback) {this .content = content;this .isFallback = isFallback;
这个例子里 thenApplyAsync 是一个很好的提示,通常我们都会使用 thenApply-习惯成自然,但是在 io client 里使用很容易让 apply 在 outbound io 线程里使用,这时候一着不慎就会阻塞 outbound io 线程。所以有意识地使用 thenApplyAsync 是一个好习惯 。
基于纵横分类的例子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 import java.util.concurrent.*;import java.util.function.BiFunction;import java.util.function.Function;public class SimpleCompletableFutureExamples {private static final ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3 , r -> {Thread t = new Thread (r, "worker-thread" );true );return t;public static void applyExamples () {"=== 产出型(apply)示例 ===" );"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 生产者: 生成初始值" );return 42 ;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 产出型: 转换 " + number + " -> 字符串" );return "Value: " + number;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 生产者: 生成第二个值" );return 100 ;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 产出型: 合并 " + num1 + " 和 " + num2);return "Sum: " + (num1 + num2);"结果1: " + future2.join());"结果2: " + combined.join());public static void acceptExamples () {"\n=== 消耗型(accept)示例 ===" );"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 生产者: 生成数据" );return "Hello World" ;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 消耗型: 记录日志 - " + result);"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 生产者: 生成第二个数据" );return "Java" ;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 消耗型: 同时消费两个结果 - " + result1 + ", " + result2);public static void runExamples () {"\n=== 无消费无产出型(run)示例 ===" );"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 生产者: 生成数据" );return "Data" ;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 无消费无产出: 发送通知(不依赖结果)" );"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 生产者: 生成第二个数据" );return "More Data" ;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 无消费无产出: 两个任务完成,清理资源" );public static void composeExamples () {"\n=== 组合型(compose)示例 ===" );"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 阶段1: 生成初始值" );return 10 ;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 组合型: 阶段1完成,值=" + value);return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 阶段2: 基于阶段1的值计算" );return value * 2 ;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 组合型: 阶段2完成,值=" + value);return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 阶段3: 最终计算" );return value + 5 ;"最终结果: " + stage3.join());public static void exceptionExamples () {"\n=== 异常处理示例 ===" );"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 模拟失败的操作" );throw new RuntimeException ("操作失败" );"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 异常处理: exceptionally - " + ex.getMessage());return "降级结果" ;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 可能成功或失败的操作" );return Math.random() > 0.5 ? "成功结果" : null ; if (ex != null ) {"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 异常处理: handle - 捕获异常" );return "处理后的异常结果" ;else {"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 异常处理: handle - 正常结果" );return "处理后的成功结果: " + result;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 需要记录日志的操作" );return "需要日志的结果" ;if (ex != null ) {"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 异常处理: whenComplete - 记录异常" );else {"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 异常处理: whenComplete - 记录结果: " + result);"日志记录后的降级结果" );"exceptionally 结果: " + fallbackFuture.join());"handle 结果: " + handleFuture.join());"whenComplete 结果: " + loggingFuture.join());public static void producerConsumerExample () {"\n=== 最简生产者-消费者模型 ===" );"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 🌱 生产者: 生成数据" );try { Thread.sleep(100 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); }return "生产的数据" ;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 👥 消费者1: 转换数据 - " + data);return data.toUpperCase();"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 👥 消费者2: 消费数据 - " + data);"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 👥 消费者3: 开始组合处理" );return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 👥 消费者3: 异步处理 " + data);return data + "-processed" ;"✅ 所有消费者完成" ))"消费者1最终结果: " + consumer1.join());"消费者3最终结果: " + consumer3.join());public static void main (String[] args) {try {"\n✅ 所有 CompletableFuture API 示例执行完成" );"✨ 架构验证: 横向分类 + 纵向分类" );finally {
exceptionally
graph LR
A[原始 CompletableFuture] -->|正常完成| B[“成功值”]
A -->|异常完成| C[RuntimeException]
B --> D[套壳 CompletableFuture]
C -->|fn.apply| E[“降级值”]
E --> D
D -->|总是正常完成| F[最终结果]1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 import java.util.concurrent.*;import java.util.function.Function;public class ExceptionallyPrinciples {private static final ExecutorService bizPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2 , r -> {Thread t = new Thread (r, "biz-thread" );true );return t;public static void main (String[] args) {"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 🌐 调用外部服务 (模拟失败)" );throw new RuntimeException ("网络超时: 服务不可用" );String result = serviceCall"❌ 这行永远不会执行! (thenApply被跳过)" );return data.toUpperCase();"❌ 这行永远不会执行! (thenAccept被跳过)" );"❌ 这行永远不会执行! (第二个thenApply被跳过)" );return data + "_PROCESSED" ;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] ✅ 原则1: 就近逃生 - 捕获网络异常: " + ex.getMessage());if (ex.getCause().getMessage().contains("网络" )) {return "NEAR_FALLBACK" ; throw ex;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] ✅ 原则2: 状态重置 - 当前值: '" + value + "' (状态已正常化)" );return value + "_ENHANCED" ;if (value.contains("FAIL" )) {throw new RuntimeException ("处理阶段异常" );return value;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] ⚠️ 原则3: 线程陷阱 - 在" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行降级" );try { Thread.sleep(50 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); }return "TRAP_FALLBACK" ;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] ✅ 原则4: 信息保留 - 原始异常: " + null ? ex.getCause().getMessage() : ex.getMessage()));return "PRESERVED:" + (ex.getCause() != null ? ex.getCause().getClass().getSimpleName() : ex.getClass().getSimpleName());"\n🎯 最终结果: '" + result + "'" );private static String handleBusinessException (Throwable ex) {"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] ✅ 原则5: 业务异常处理 - 检查: " + ex.getMessage());if (ex.getMessage().contains("业务" ) || ex.getCause().getMessage().contains("业务" )) {"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] → 业务异常匹配,返回降级值" );return "BUSINESS_FALLBACK" ;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] → 非业务异常,透传给下一层" );throw new CompletionException (ex); private static String handleSystemException (Throwable ex) {"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] ✅ 原则5: 系统异常处理 - 检查: " + ex.getMessage());String errorMsg = ex.getMessage() + (ex.getCause() != null ? ex.getCause().getMessage() : "" );if (errorMsg.contains("网络" ) || errorMsg.contains("超时" ) || errorMsg.contains("IO" )) {"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] → 系统异常匹配,返回降级值" );return "SYSTEM_FALLBACK" ;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] → 非系统异常,透传给兜底层" );throw new CompletionException (ex); private static String ultimateFallback (Throwable ex) {"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] ✅ 原则5: 终极兜底 - 处理所有未捕获异常: " + ex.getClass().getSimpleName());return "MAX_SAFETY:" + ex.getClass().getSimpleName();
allOf().thenApply(Async) 中的 join() 永不阻塞
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 import java.util.*;import java.util.concurrent.*;import java.util.stream.Collectors;import java.util.stream.IntStream;public class CompletionGuaranteePrinciple {public static void main (String[] args) {ExecutorService ioPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4 , r -> {Thread t = new Thread (r, "io-thread" );true );return t;ExecutorService cpuPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Thread t = new Thread (r, "cpu-thread" );true );return t;try {"🚀 启动完成保证原则演示\n" );0 , 10 )"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 💡 服务调用 #" + i + " 开始执行" );if (i == 5 ) {throw new RuntimeException ("服务 #5 模拟故障" );return "Result-" + i;new CompletableFuture [0 ])) "\n✅ 原则验证: 所有服务调用已完成,开始聚合结果" );"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] 🧮 聚合阶段启动(CPU密集型)" );long start = System.nanoTime();String result = future.join(); long duration = System.nanoTime() - start;"[%s] ⚡ join() 耗时: %d ns, 结果: %s\n" , return result;return results;"[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] ❌ 全局异常: " + ex.getMessage());return Arrays.asList("GLOBAL_FALLBACK" );"\n🎯 最终聚合结果: " + results.size() + " 个结果" );" - " + r));finally {private static void simulateIoOperation (int id) {try {int delay = 50 + (id * 10 ) % 200 ;catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException ("IO操作被中断" , e);
对传统的线程池的效率改进
CompletableFuture 相对于一般线程池的改进主要来自于对于复杂结果编排的 API 优化,本身并不提供性能优化 。
如果要实现性能优化,可以
基于 Netty/NIO 实现了真正的异步 RPC:
发起调用后立即返回,不阻塞线程;
结果由 Netty 的 IO 线程(或专用回调线程)在数据到达时触发;
一个 IO 线程可同时管理成千上万个连接(C10K+)。
CompletableFuture 被用作“胶水层”:
将 NIO 回调封装为 CompletableFuture(如 toCompletableFuture 工具方法);
用 thenCompose / allOf 等组合多个异步 RPC;
业务逻辑不再关心回调注册,只关注数据流依赖。
graph TD
A["Client Request"] --> B["Inbound IO Thread<br>Netty EventLoop"]
B --> C["Business Worker Thread<br>from biz-pool"]
C --> d1["Create CF1 = new CompletableFuture()"]
C --> d2["Create CF2 = new CompletableFuture()"]
C --> d3["Create CF3 = new CompletableFuture()"]
d1 --> e1["Register Observer1:<br>onSuccess → CF1.complete(...)<br>onFailure → CF1.completeEx(...)"]
d2 --> e2["Register Observer2:<br>onSuccess → CF2.complete(...)<br>onFailure → CF2.completeEx(...)"]
d3 --> e3["Register Observer3:<br>onSuccess → CF3.complete(...)<br>onFailure → CF3.completeEx(...)"]
e1 --> f1["Call mtthrift.async(orderService, Observer1)"]
e2 --> f2["Call mtthrift.async(productService, Observer2)"]
e3 --> f3["Call mtthrift.async(deliveryService, Observer3)"]
f1 --> g["Outbound IO Thread<br>Netty Client EventLoop"]
f2 --> g
f3 --> g
g --> h1["(orderService)"]
g --> h2["(productService)"]
g --> h3["(deliveryService)"]
h1 -->|Response| i1["Outbound IO Thread invokes<br>Observer1.onSuccess(result)"]
h2 -->|Response| i2["Outbound IO Thread invokes<br>Observer2.onSuccess(result)"]
h3 -->|Error| i3["Outbound IO Thread invokes<br>Observer3.onFailure(ex)"]
i1 --> j1["CF1.complete(result)"]
i2 --> j2["CF2.complete(result)"]
i3 --> j3["CF3.completeExceptionally(ex)"]
j1 --> k1["CF1.thenApplyAsync(enrichOrder, cpu-pool)"]
j2 --> k2["CF2.thenApplyAsync(enrichProduct, cpu-pool)"]
j3 --> k3["CF3.exceptionally(handleFallback)"]
k1 --> l["CF4 = CF1.thenCombine(CF2, merge)"]
k2 --> l
k1 --> m["CompletableFuture.allOf(CF1..CF30)"]
k2 --> m
k3 --> m
m --> n["m.thenApplyAsync(aggregateAll, cpu-pool)"]
n --> o["Final Result"]
o --> p["Write Response via Inbound IO Thread"]
p --> q["Client"]
classDef io fill:#d5e8d4,stroke:#82b366;
classDef worker fill:#dae8fc,stroke:#6c8ebf;
classDef outbound fill:#e1d5e7,stroke:#9673a6;
classDef cf fill:#fff2cc,stroke:#d6b656;
classDef service fill:#f8cecc,stroke:#b85450;
classDef observer fill:#e6e6fa,stroke:#999;
class B,p io
class C,d1,d2,d3,e1,e2,e3,f1,f2,f3,k1,k2,k3,l,m,n worker
class g,i1,i2,i3 outbound
class j1,j2,j3,o cf
class h1,h2,h3 service
class e1,e2,e3 observerRxJava
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#E1D5E7', 'edgeLabelBackground':'#FFF', 'fontFamily': 'monospace'}}}%%
sequenceDiagram
participant Client as Client
participant Observable as Observable
participant Operator1 as map
participant Operator2 as filter
participant Subscriber as Subscriber
Note over Client,Subscriber: RxJava (响应式流)
Client->>Observable: create(emitter)
Observable-->>Operator1: 注册操作符
Operator1->>Observable: map(transform)
Observable-->>Operator2: 注册操作符
Operator2->>Observable: filter(predicate)
Observable-->>Subscriber: subscribe(Subscriber)
Note right of Client: 非阻塞订阅
par 数据流处理
Observable->>Operator1: onNext(item)
Operator1->>Operator2: onNext(mapped)
Operator2->>Subscriber: onNext(filtered)
end
Observable->>Subscriber: onComplete()
Note over Client: 响应式: map/filter/subscribe1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 1000 );return "Hello" ;500 );return "RxJava" ;" " + s2)2 , TimeUnit.SECONDS)"FALLBACK: " + ex.getMessage())"结果: " + result),"错误: " + error.getMessage())
Reactor
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#9DC3E6', 'edgeLabelBackground':'#FFF', 'fontFamily': 'monospace'}}}%%
sequenceDiagram
participant Client as Client
participant Flux as Flux
participant Operator1 as map
participant Operator2 as flatMap
participant Subscriber as Subscriber
Note over Client,Subscriber: Reactor (响应式流)
Client->>Flux: create(sink)
Flux-->>Operator1: 注册操作符
Operator1->>Flux: map(transform)
Flux-->>Operator2: 注册操作符
Operator2->>Flux: flatMap(asyncOp)
Flux-->>Subscriber: subscribe(Subscriber)
Note right of Client: 非阻塞订阅
par 数据流处理
Flux->>Operator1: onNext(item)
Operator1->>Operator2: onNext(mapped)
Operator2->>Subscriber: onNext(result)
end
Flux->>Subscriber: onComplete()
Note over Client: 响应式: map/flatMap/subscribe1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 1000 );return "Hello" ;500 );return "Reactor" ;" " + s2)2 ))"FALLBACK: " + ex.getMessage()))"结果: " + result),"错误: " + error.getMessage()),"完成" )