Java 的原生注解
@Inherited
@Inherited 是一个元注解 (annotations applied to other annotations 注解其他注解的注解),也是一个标记注解,@Inherited阐述了某个被标注的类型是被继承的。 **@Inherited annotation类型是被标注过的class的子类所继承。类并不从它所实现的接口继承annotation,方法并不从它所重载的方法继承annotation。**其查找过程是:反射 API 会在查找 @Inherited 标注的注解的时候,自底向上往继承树上方查找。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 @Inherited @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.TYPE) public @interface MyAnnotation {value () default "Default Value" ;@MyAnnotation(value = "Parent Class") public class ParentClass {public class ChildClass extends ParentClass {ChildClass child = new ChildClass ();MyAnnotation annotation = ChildClass.class.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);if (annotation != null ) {
@Inherited 仅适用于类,对方法、属性或构造函数的注解无效。
子类可以定义同名注解来覆盖继承的注解。在上面的例子里面,@MyAnnotation(value = “Parent Class”)在子类里应该可以重新赋值成 @MyAnnotation(value = “Child Class”)
接口中的注解不会被子类继承,即使注解使用了 @Inherited。
如果一个类实现了一个接口,那么这个类不会继承接口中定义的任何注解。
WebSocket 注解相关的争论
[jsr356-experts] Annotation inheritance: was: Re: Potpourri of smaller issues
这个争论的问题是:
@WebSocketMessage 可被继承吗?看起来是不可以的,因为这不是一个类注解
@WebSocketEndpoint(/“chat”) 是一个类注解,这个类注解被子类覆盖 @WebSocketEndpoint(/“superchat”) 以后。有几个 endpoint?实际上可能是只有1个(覆盖的 semantics)就是这样,但也许 chat 是一个必须存在的endpoint,不能被覆盖,那么是不是无意中覆盖它会有问题,这是不是带来了一个不能扩展但又不是 final 的类型?
其他元注解
@Target: Describes the targets to which an annotation can be applied; this directly corresponds to the nine contexts above
@Retention: Describes how long the annotation should be retained by the compiler
@Inherited: Denotes that an annotation should be inherited by a subtype if applied to a supertype
@Deprecated: Denotes that an annotation (or any other type) should no longer be used
@Repeatable: Denotes that an annotation can be applied multiple times in the same context; i.e. a class can have the same annotation applied to it two or more times 这一种注解最有意思,但平时没有什么用例,其大部分使用场景可以被一个复合值的 values 代替。
注意,直接在注解上加入注解,实际上就产生了组合注解,会让配置集体生效,但这和继承元注解不一样。
Spring 原生的功能
xml 的模式
spring 的配置总是:
有固定值的 w3c 的 xsi
beans ns 它属于 spring org 的 schema 的一个子目录
多个 attribute ns (它实际上是一个目录)
一个 attirbute schemaLocation(它是目录里面的真正方定义的地方) 它也属于 spring org 的 schema 的一个子目录,通常是一段 xsd
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" <!-- w3c 的 xsi ,默认总有 -- >
带有 name 的注解
1 2 3 4 5 @Repository("movieDao") @Bean("writer2") @Transactional(value="txManager1")
@Configuration
@Configuration 注解本质上还是 @Component,但又不同于 @Component,详见《Spring @Configuration 和 @Component 区别 。@Configuration 里的 @Bean 方法可以嵌套使用,而@Component 里的 @Bean 方法不可以。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Component @Configuration public class AppConfig {@Bean public MyBean myBean () {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ();MyBean myBean = ctx.getBean(MyBean.class);@Configuration @ComponentScan(value = "com.acme.app.services",excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }) public class AppConfig {@Configuration @PropertySource("classpath:/com/acme/app.properties") @PropertySource("classpath:bar.properties") @PropertySources({ @PropertySource("classpath:foo.properties"), @PropertySource("classpath:bar.properties") }) public class AppConfig {@Value( "${jdbc.url:aDefaultUrl}" ) private String jdbcUrl;@Value("${bean.name}") String beanName;@Bean public MyBean myBean () {return new MyBean (beanName);@Configuration @Import(DatabaseConfig.class) public class AppConfig {private final DatabaseConfig dataConfig;public AppConfig (DatabaseConfig dataConfig) {this .dataConfig = dataConfig;@Bean public MyBean myBean () {return new MyBean (dataConfig.dataSource());@Configuration @ImportResource(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"}) public class XmlConfiguration {@Profile("development") @Configuration public class EmbeddedDatabaseConfig {@Bean public DataSource dataSource () {@Profile("production") @Configuration public class ProductionDatabaseConfig {@Bean public DataSource dataSource () {@Configuration public class ProfileDatabaseConfig {@Bean("dataSource") @Profile("development") public DataSource embeddedDatabase () { ... }@Bean("dataSource") @Profile("production") public DataSource productionDatabase () { ... }@Configuration public class AppConfig {@Inject DataSource dataSource;@Bean public MyBean myBean () {return new MyBean (dataSource);@Configuration static class DatabaseConfig {@Bean dataSource () {return new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder ().build();@Lazy @Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.baeldung.lazy") public class AppConfig {@Bean public Region getRegion () {return new Region ();@Bean public Country getCountry () {return new Country ();
@EnableAsync
激活异步拦截器,类似美团的 mole。
参考《How To Do @Async in Spring》 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 @Configuration @EnableAsync public class AppConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {@Override public Executor getAsyncExecutor () {ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor ();7 );42 );11 );"MyExecutor-" );return executor;@Override public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler () {return new MyAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler ();@Bean public MyAsyncBean asyncBean () {return new MyAsyncBean ();public class MyAsyncBean {@Async("threadPoolTaskExecutor") public void asyncMethodWithConfiguredExecutor () {"Execute method with configured executor - " @Async public Future<String> asyncMethodWithReturnType () {"Execute method asynchronously - " try {5000 );return new AsyncResult <String>("hello world !!!!" );catch (InterruptedException e) {return null ;public class CustomAsyncExceptionHandler implements AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler {@Override public void handleUncaughtException ( Throwable throwable, Method method, Object... obj) {"Exception message - " + throwable.getMessage());"Method name - " + method.getName());for (Object param : obj) {"Parameter value - " + param);
对应的 xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <beans > <task:annotation-driven executor ="myExecutor" exception-handler ="exceptionHandler" /> <task:executor id ="myExecutor" pool-size ="7-42" queue-capacity ="11" /> <bean id ="asyncBean" class ="com.foo.MyAsyncBean" /> <bean id ="exceptionHandler" class ="com.foo.MyAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler" /> </beans >
@EnableScheduling
激活任务调度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 @Configuration @EnableScheduling public class AppConfig {@Scheduled(fixedRate=1000) public void work () {public class MyTask {@Scheduled(fixedRate=1000) public void work () {@Configuration @EnableScheduling public class AppConfig implements SchedulingConfigurer {@Override public void configureTasks (ScheduledTaskRegistrar taskRegistrar) {@Bean(destroyMethod="shutdown") public Executor taskExecutor () {return Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(100 );@Override public void configureTasks (ScheduledTaskRegistrar taskRegistrar) {new Runnable () {public void run () {new CustomTrigger ()@Bean(destroyMethod="shutdown") public Executor taskScheduler () {return Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(42 );@Bean public MyTask myTask () {return new MyTask ();
对应的 xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:task ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/task http://www.springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task-3.2.xsd" ><task:annotation-driven executor ="jobExecutor" scheduler ="jobScheduler" /> <task:executor id ="jobExecutor" pool-size ="5" /> <task:scheduler id ="jobScheduler" pool-size ="10" /> </beans >
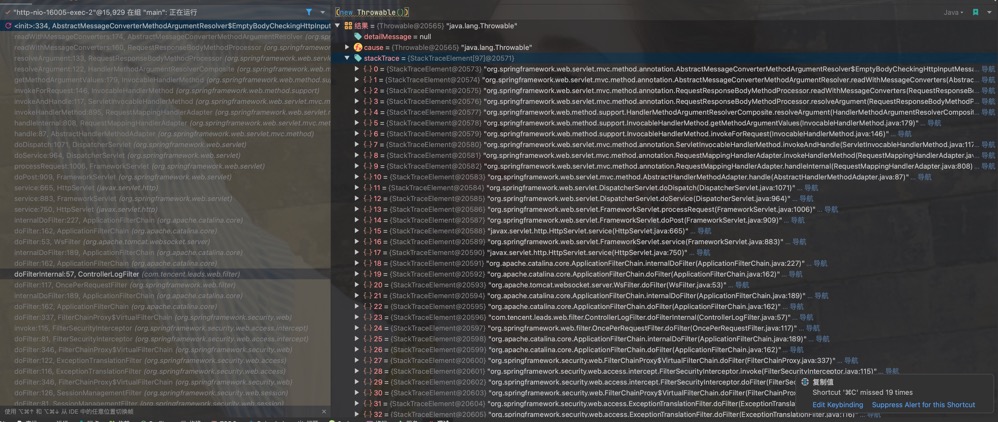
@EnableTransactionManagement
TransactionInterceptor 是被 proxy 或者 advice 加入到调用栈中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @Configuration @EnableTransactionManagement public class AppConfig {@Bean public FooRepository fooRepository () {return new JdbcFooRepository (dataSource());@Bean public DataSource dataSource () {@Bean public PlatformTransactionManager txManager () {return new DataSourceTransactionManager (dataSource());
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <beans > <tx:annotation-driven /> <bean id ="fooRepository" class ="com.foo.JdbcFooRepository" > <constructor-arg ref ="dataSource" /> </bean > <bean id ="dataSource" class ="com.vendor.VendorDataSource" /> <bean id ="transactionManager" class ="org.sfwk...DataSourceTransactionManager" > <constructor-arg ref ="dataSource" /> </bean > </beans >
Please note that proxy mode allows for interception of calls through the proxy only; local calls within the same class cannot get intercepted that way.
Note that if the mode() is set to AdviceMode.ASPECTJ, then the value of the proxyTargetClass() attribute will be ignored. Note also that in this case the spring-aspects module JAR must be present on the classpath, with compile-time weaving or load-time weaving applying the aspect to the affected classes. There is no proxy involved in such a scenario; local calls will be intercepted as well.
aspectj 的织入可以增强本地调用,默认的 proxy mode 不可以。
AdviceMode.PROXY
各种 mode 的解释见《Optimal @EnableTransactionManagement Configuration》 ,必须配合proxyTargetClass配置使用:
This configuration says how the transaction aspect will be applied.
adviceMode=proxy, proxyTargetClass=true Cglib is used as proxy
adviceMode=proxy, proxyTargetClass=false Jdk proxy mechanism is used.
So, for adviceMode=proxy, the decision relies more on how are your
adviceMode=aspectJ uses aspectJ library, which does byte code
adviceMode=aspectJ, compile-time weaving You should incorporate
adviceMode=aspectJ, load-time weaving Instrumentation is performed on
Using aspectJ is more powerful and probably more performant. It is
基本上静态织入的 AspectJ 的性能最好(我们大多数时候都习惯使用 compile-time-weaving,但其实 AspectJ 还支持 load-time-weaving),但平时我们用得最多的还是 cglib 生成的 proxy(因为 Spring 会自动帮我们决策最优的方案)。
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 @Configuration @EnableAspectJAutoProxy public class AppConfig {@Bean public FooService fooService () {return new FooService ();@Bean public MyAspect myAspect () {return new MyAspect ();@Aspect public class MyAspect {@Before("execution(* FooService+.*(..))") public void advice () {
web application context 和 DispatcherServlet application contexts 是两个 context,需要单独声明 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy at multiple levels。
@EnableWebMvc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @Configuration @EnableWebMvc @ComponentScan( basePackageClasses = { MyConfiguration.class }, excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, value = Configuration.class) } ) public class MyConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {@Override public void addFormatters (FormatterRegistry formatterRegistry) {new MyConverter ());@Override public void configureMessageConverters (List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {new MyHttpMessageConverter ());
ContextConfiguration
spring-test特有,ContextConfiguration 要和@Configuration或者@Component配合使用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @TestPropertySource("/foo.properties") @ContextConfiguration(classes = {AppConfig.class, DatabaseConfig.class}) @TestPropertySource(properties = {"foo=bar"}) @SpringBootTest(properties = {"foo=bar"}, classes = SpringBootPropertiesTestApplication.class) public class MyTests {@Autowired MyBean myBean;@Autowired DataSource dataSource;@Test public void test () {
@PropertySource
property 跨上下文继承的关系见《Properties with Spring and Spring Boot》 。《官方的列表》 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Configuration @PropertySource("classpath:/com/acme/app.properties") public class AppConfig {@Inject Environment env;@Bean public MyBean myBean () {return new MyBean (env.getProperty("bean.name" ));
@ComponentScan
它指定的扫描属性依赖于 basePackageClasses()/basePackages() (or its alias value()。
环境 API
环境 API 意味着对 properties 和 profile 的建模,Environment接口扩展了PropertyResolver接口。
参考《Spring的Property配置加载和使用过程及Environment的初始化过程 :
首先,PropertySource其实就是包装的具体配置,跟Properties差不多。
而PropertyResolver,就是用于对PropertySource进行特殊处理,比如解析holder、转换值的类型等。
Spring启动时,默认会new一个StandardEnvironment,这个类里面就默认添加了两个PropertySource(SystemProperties和SystemEnvironment,分别对应System.getenv和System.getProperty)
注意,可能是为了使用方便,Environment实现了PropertyResolver接口。
每一个参数,但凡可以用-D 动态传入,也应该可以使用环境变量,甚至 JNDI 的配置,其相对顺序参考《Spring Boot Configuration Priority order》 :
command-line arguments.
The Java system parameters obtained through System.getproperties ().
Operating system environment variables.
The JNDI attribute obtained from java:comp/env.
The “random.*” property generated by Randomvaluepropertysource.
Apply the properties file outside of the Jar file . (via
spring.config.location parameter)
Apply the properties file inside the Jar file.
A property file that is declared through the “@PropertySource”
annotation in the application Configuration Java class (the Java
class that contains the “@Configuration” annotations).
The default property declared by the “Springapplication.setdefaultproperties”.
在 java 中获取环境变量:环境变量System.getenv() 或者 environment.getenv()
System.getenv() 方法是获取指定的环境变量的值。它有两种方法,一种是接收参数为任意字符串,当存在指定环境变量时即返回环境变量的值,否则返回null。另外一种是不接受参数,那么返回的是所有的环境变量。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public static String getenv (String name) {SecurityManager sm = getSecurityManager();if (sm != null ) {new RuntimePermission ("getenv." +name));return ProcessEnvironment.getenv(name);public static java.util.Map<String,String> getenv () {SecurityManager sm = getSecurityManager();if (sm != null ) {new RuntimePermission ("getenv.*" ));return ProcessEnvironment.getenv();
在 java 中获取属性:System.getProperty() 或者 environment.getProperty()
获取系统的相关属性,包括文件编码、操作系统名称、区域、用户名等,此属性一般由jvm自动获取,不能设置。这个必须接受一个String类型的参数,返回值的类型也是String,如果想获取所有的系统的相关属性值可以使用System.getProperties()
java.version Java 运行时环境版本java.vm.specification.name Java 虚拟机规范名称java.vm.name Java 虚拟机实现名称java.specification.name Java 运行时环境规范名称os.name 操作系统的名称user.name 用户的账户名称
对应的命令行用法是java -jar jarName -DpropertyName=value,如java -Djavadoop.database.password=admin4321 -jar app.jar。
参考《System.getenv()和System.getProperty() 的区别》 。
profile 的定义
a named, logical group of bean definitions to be registered with the
和 Configuration 类似,用来聚合 bean。与之相对应地,maven 中的 profile 就是用来聚合配置用的 。一旦被注册进了某个 profile,则 bean 不会轻易地被默认激活。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 @Component @Profile("dev") public class DevDatasourceConfig @Component @Profile("!dev") public class DevDatasourceConfig @Configuration public class MyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {@Override public void onStartup (ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {"spring.profiles.active" , "dev" );@Autowired private ConfigurableEnvironment env;"someProfile" );
properties 的例子
properties files, JVM system properties, system environment variables,
所有的 properties 都由PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer对${}进行注入。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Configuration public class AppConfig {@Autowired Environment env;@Bean public MyBean myBean () {MyBean myBean = new MyBean ();"bean.name" ));return myBean;
Aware 接口
ApplicationContextAware
ApplicationEventPublisherAware
BeanClassLoaderAware
BeanFactoryAware
BeanNameAware
BootstrapContextAware
EmbeddedValueResolverAware
EnvironmentAware
ImportAware
LoadTimeWeaverAware
MessageSourceAware
NotificationPublisherAware
ResourceLoaderAware
SchedulerContextAware
ServletConfigAware
ServletContextAware
其中PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer是Spring3.1之前使用的。
有了这个机制,才能让特定的 .properties 注入到特定的 xml 占位符里面。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 <bean id ="propertyConfigurer" class ="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer" > <property name ="location" > <value > conf/sqlmap/jdbc.properties</value > </property > <property name ="fileEncoding" > <value > UTF-8</value > </property > </bean > <bean id ="propertyConfigurer" class ="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer" > <property name ="locations" > <list > <value > /WEB-INF/mail.properties</value > <value > classpath: conf/sqlmap/jdbc.properties</value > //注意这两种value值的写法</list > </property > </bean > <context:property-placeholder location ="classpath*:/WEB-INF/mail.properties" />
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer本质上是一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor。解析XML的流程在BeanFactoryPostProcessor之前, 优先将配置文件的路径以及名字通过Setter传入PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer。
如上BeanFactoryPostProcessor的优先级又优于其余的Bean。因此可以实现在bean初始化之前的注入。
参考:
《Spring PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer工作原理》 《Spring 常用的两种PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer》 基本还是 MergedProperties 那一套。《Spring Properties Loader》
xml 配置
annotation-config等字符串实际上指的是一个 element 的 attribute。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd" profile ="dev" ><context:component-scan base-package ="com.xh.spring.aop" > <context:include-filter type ="annotation" expression ="org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect" /> <context:exclude-filter type ="annotation" expression ="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" /><context:exclude-filter type ="annotation" expression ="org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController" /></context:component-scan > <context:annotation-config /> <context:property-placeholder ignore-unresolvable ="true" location ="classpath*:/base.properties,classpath:database.properties" /> <mvc:annotation-driven /> <aop:config proxy-target-class ="true" > <aop:aspect id ="log" ref ="logHandler" > <aop:pointcut id ="printLog" expression ="execution(* cn.sw.study.common.test.spring.aop.service..*(..))" /> <aop:before method ="LogBefore" pointcut-ref ="printLog" /> <aop:after method ="LogAfter" pointcut-ref ="printLog" /> </aop:aspect > </aop:config > <bean class ="com.acme.AppConfig" /> <bean id ="propBean" class ="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertiesFactoryBean" > <property name ="locations" value ="classpath:jdbc.properties" /> </bean > <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager ="transactionManager" /> <bean id ="transactionManager" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" > <property name ="dataSource" > <ref bean ="routingDatasource" /> </property > </bean > <import resource ="a.xml" /> <import resource ="b.xml" /> <import resource ="springmvc-web.xml" /> </beans > <context:component-scan /> <context:property-placeholder /> <context:property-placeholder location ="classpath*:/WEB-INF/mail.properties" />
@ResponseBody
表示该方法的返回结果直接写入HTTP response body中,一般在异步获取数据时使用,在使用@RequestMapping后,返回值通常解析为跳转路径,
加上@responsebody后返回结果不会被解析为跳转路径,而是直接写入HTTP response body中;比如异步获取json数据,加上@responsebody后,会直接返回json数据;
@RequestBody
参数前加上这个注解之后,认为该参数必填。表示接受json字符串转为对象 List等;
@Qualifier
当有多个同一类型的Bean时,可以用@Qualifier(“name”)来指定。与@Autowired配合使用
@Autowired
按照类型(byType)装配依赖对象,默认情况下它要求依赖对象必须存在,如果允许null值,可以设置它的required属性为false。如果我们想使用按照名称(byName)来装配,可以结合@Qualifier注解一起使用。(通过类型匹配找到多个candidate,在没有@Qualifier、@Primary注解的情况下,会使用对象名作为最后的fallback匹配)。
@Resource
1 @Resource(name=”name”,type=”type”)
默认按照ByName自动注入,由J2EE提供,需要导入包javax.annotation.Resource。@Resource有两个重要的属性:name和type,而Spring将@Resource注解的name属性解析为bean的名字,而type属性则解析为bean的类型。所以,如果使用name属性,则使用byName的自动注入策略,而使用type属性时则使用byType自动注入策略。如果既不制定name也不制定type属性,这时将通过反射机制使用byName自动注入策略。
@RequestMapping
RequestMapping是一个用来处理请求地址映射的注解,可用于类或方法上。用于类上,表示类中的所有响应请求的方法都是以该地址作为父路径;
params:指定request中必须包含某些参数值是,才让该方法处理。
它还有其他语法糖:@GetMapping、@PostMapping
@RequestParam
用在方法的参数前面。相当于 request.getParameter;
@PathVariable
路径变量。如 RequestMapping(“user/get/mac/{macAddress}”) ;
public String getByMacAddress(
@ControllerAdvice
@ControllerAdvice是一个特殊的 @Component,用于标识一个类,这个类中被以下三种注解标识的方法:@ExceptionHandler,@InitBinder,@ModelAttribute,将作用于所有的@Controller类的接口上。这三种方法,可以被认为是三种 advice。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 @ControllerAdvice public class ActionAdvice {@InitBinder public void handleException (WebDataBinder binder) {new DateFormatter ("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss" ));@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) @ResponseBody @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) public Map handleException (Exception ex) {new HashMap <>();"code" , 400 );"msg" , ex.toString());return map;@RestController public class BasicController {@GetMapping(value = "index") public Map index (@ModelAttribute("user") String user) {
DelegatingFilterProxy
过滤器,它指向一个bean,这个bean在spring中的名字为testBean,testBean也必需实现javax.servlet.Filter。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 <filter > <filter-name > testFilter</filter-name > <filter-class > org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class > <init-param > <param-name > targetBeanName</param-name > <param-value > testBean</param-value > </init-param > <init-param > <param-name > contextAttribute</param-name > <param-value > session</param-value > </init-param > <init-param > <param-name > targetFilterLifecycle</param-name > <param-value > false</param-value > </init-param > </filter > <filter-mapping > <filter-name > testFilter</filter-name > <url-pattern > /*</url-pattern > </filter-mapping >
JPA 特性
JPA注解式配置.xmind
@Table
@Table(name=”“)
@MappedSuperClass
用在确定是父类的entity上。父类的属性子类可以继承;
@NoRepositoryBean
一般用作父类的repository,有这个注解,spring不会去实例化该repository;
@Column
如果字段名与列名相同,则可以省略;
@Id
表示该属性为主键;
@GeneratedValue
1 @GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.SEQUENCE,generator = “repair_seq”)
表示主键生成策略是sequence(可以为Auto、IDENTITY、native等,Auto表示可在多个数据库间切换),指定sequence的名字是repair_seq;
参考《JPA 的 id 生成策略》 。
@SequenceGeneretor
1 @SequenceGeneretor(name = “repair_seq”, sequenceName = “seq_repair”, allocationSize = 1)
name为sequence的名称,以便使用,sequenceName为数据库的 sequence 名称,两个名称可以一致;
要底层的 RDBMS 能够支持 sequence 功能。
@Transient
表示该属性并非一个到数据库表的字段的映射,ORM框架将忽略该属性.
如果一个属性并非数据库表的字段映射,就务必将其标示为@Transient,否则,ORM框架默认其注解为@Basic;
@Basic(fetch=FetchType.LAZY)
1 @Basic(fetch=FetchType.LAZY)
标记可以指定实体属性的加载方式;
@JsonIgnore
作用是json序列化时将java bean中的一些属性忽略掉,序列化和反序列化都受影响
@JoinColumn(name=”loginId”)
1 @JoinColumn(name=”loginId”)
一对一:本表中指向另一个表的外键。
表之间的映射
对应Hibernate配置文件中的一对一,一对多,多对一。
哪一边是 owning side 很重要。
OneToOne
Implementing with a Foreign Key in JPA
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 @Entity @Table(name = "users") public class User {@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) @Column(name = "id") private Long id;@OneToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL) @JoinColumn(name = "address_id", referencedColumnName = "id") private Address address;@Entity @Table(name = "address") public class Address {@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) @Column(name = "id") private Long id;@OneToOne(mappedBy = "address") private User user;
Implementing with a Shared Primary Key in JPA
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 @Entity @Table(name = "users") public class User {@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) @Column(name = "id") private Long id;@OneToOne(mappedBy = "user", cascade = CascadeType.ALL) private Address address;@Entity @Table(name = "address") public class Address {@Id @Column(name = "id") private Long id;@OneToOne @MapsId private User user;
Modeling with a Join Table
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 @Entity @Table(name = "employee") public class Employee {@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) @Column(name = "id") private Long id;@OneToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL) @JoinTable(name = "emp_workstation", joinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "employee_id", referencedColumnName = "id") }, inverseJoinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "workstation_id", referencedColumnName = "id") }) private WorkStation workStation;@Entity @Table(name = "workstation") public class WorkStation {@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) @Column(name = "id") private Long id;@OneToOne(mappedBy = "workStation") private Employee employee;
@OneToMany
As stated in the JPA specification under section 2.9, it’s a good practice to mark many-to-one side as the owning side.
平凡解决方案
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 @Entity @Table(name="CART") public class Cart {@OneToMany(mappedBy="cart") private Set<Items> items;@Entity @Table(name="ITEMS") public class Items {@ManyToOne @JoinColumn(name="cart_id", nullable=false) private Cart cart;public Items () {}
Cart as the Owning Side
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class ItemsOIO {@ManyToOne @JoinColumn(name = "cart_id", insertable = false, updatable = false) private CartOIO cart;public class CartOIO {@OneToMany @JoinColumn(name = "cart_id") private Set<ItemsOIO> items;
@ManyToOne
缺,来日补上
@ManyToMany
普通映射
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 @Entity class Student {@Id @ManyToMany @JoinTable( name = "course_like", joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "student_id"), inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "course_id")) @Entity class Course {@Id @ManyToMany
Joining Table
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 @Embeddable class CourseRatingKey implements Serializable {@Column(name = "student_id") @Column(name = "course_id") @Entity class CourseRating {@EmbeddedId @ManyToOne @MapsId("student_id") @JoinColumn(name = "student_id") @ManyToOne @MapsId("course_id") @JoinColumn(name = "course_id") int rating;class Student {@OneToMany(mappedBy = "student") class Course {@OneToMany(mappedBy = "course")
Spring Boot 特性
Spring Boot 在扫描类路径的时候扫到特定的包的时候,会自动激活事务管理、Spring MVC 等功能。
@SpringBootApplication
自带其他自动化配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }) public @interface SpringBootApplication {}
@EnableAutoConfiguration
打开这个配置后,可以通过扫描类路径、配置文件自动打开某些配置。
TransactionAutoConfiguration
spring-boot 不需要打开 @EnableTransactionManagement。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration.class) @Configuration @EnableTransactionManagement protected static class TransactionManagementConfiguration {@Configuration @ConditionalOnClass(PlatformTransactionManager.class) @AutoConfigureAfter({ JtaAutoConfiguration.class, HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class, DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration.class, Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration.class }) @EnableConfigurationProperties(TransactionProperties.class) public class TransactionAutoConfiguration {@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public TransactionManagerCustomizers platformTransactionManagerCustomizers ( ObjectProvider<PlatformTransactionManagerCustomizer<?>> customizers) {return new TransactionManagerCustomizers (customizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));@Configuration @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(PlatformTransactionManager.class) public static class TransactionTemplateConfiguration {private final PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;public TransactionTemplateConfiguration (PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) {this .transactionManager = transactionManager;@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(TransactionOperations.class) public TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate () {return new TransactionTemplate (this .transactionManager);@Configuration @ConditionalOnBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration.class) public static class EnableTransactionManagementConfiguration {@Configuration @EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = false) @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "false", matchIfMissing = false) public static class JdkDynamicAutoProxyConfiguration {@Configuration @EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true) @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true) public static class CglibAutoProxyConfiguration {
这个包下面的注解都带有一个元注解:
1 @Conditional(OnJavaCondition.class)
Spring 自己有一套条件体系:
1 2 OnJavaCondition extends SpringBootCondition extends Condition
《自定义 condition 的例子》
这些注解可以放在 @Bean、@Component、乃至于一堆 bean (@Configuration)上。
@ConditionalOnBean
在早期版本有 bug,参考《深入Spring Boot:那些注入不了的Spring占位符(${}表达式)》 。
仅仅在当前上下文中存在某个 bean 时,才会初始化一个 Bean。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Component @ConditionalOnBean(name="redisTemplate") public class RedisOperBean {private final RedisTemplate redisTemplate;public RedisOperBean (RedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
@ConditionalOnClass
只有类路径里存在特定的 class 的时候,才会初始化一个 Bean。
1 2 3 4 5 @Bean @ConditionalOnClass(DependedClz.class) public LoadIfClzExists loadIfClzExists () {return new LoadIfClzExists ("dependedClz" );
只在特定的云平台是活动的时候,才会初始化一个 Bean。
1 2 3 4 CLOUD_FOUNDRY
@ConditionalOnExpression
当表达式为true的时候,才会初始化一个 Bean。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package com.roytuts.spring.conditional.on.expression;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnExpression;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration @ConditionalOnExpression(value = "${module.enabled} and ${module.submodule.enabled}") class SpringConfig {@Bean public Module module () {return new Module ();
1 2 module.enabled =true module.submodule.enabled =true
@ConditionalOnJava
只有遇到特定的 JVM version,才会初始化一个 Bean。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "websocketContainerCustomizer") @ConditionalOnJava(JavaVersion.SEVEN) public TomcatWebSocketContainerCustomizer websocketContainerCustomizer () {return new TomcatWebSocketContainerCustomizer ();
@ConditionalOnJndi
只有 jndi 路径上有特定的资源的时候,才会初始化一个 Bean。
1 2 3 4 5 @Configuration @ConditionalOnJndi("java:comp/env/foo") class OnJndiModule {
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
仅仅在当前上下文中不存在某个 bean 时,才会初始化一个 Bean。
1 2 3 4 5 @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "notExistsBean") public LoadIfBeanNotExists loadIfBeanNotExists () {return new LoadIfBeanNotExists ("notExistsBean" );
@ConditionalOnMissingClass
class不存在时,才会初始化一个 Bean。
1 2 3 4 5 @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingClass("com.git.hui.boot.conditionbean.example.depends.clz.DependedClz") public LoadIfClzNotExists loadIfClzNotExists () {return new LoadIfClzNotExists ("com.git.hui.boot.conditionbean.example.depends.clz.DependedClz" );
@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication
只有 application context 不是一个 web application context 时,才会初始化一个 Bean。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package com.roytuts.spring.conditional.on.web.notweb.application;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnWebApplication;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration @ConditionalOnWebApplication class SpringConfigOnWebNotWebApp {@Bean public Module module () {return new Module ();
@ConditionalOnProperty
特定的属性有特定的值的时候,才会初始化一个 Bean。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Configuration @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix="mf",name = "assert", havingValue = "true") public class AssertConfig {@Autowired private HelloServiceProperties helloServiceProperties;@Bean public HelloService helloService () {HelloService helloService = new HelloService ();return helloService;
@ConditionalOnResource
只有特定的(非 JNDI)资源存在的时候,才会初始化一个 Bean。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @ConditionalOnResource(resources = "classpath:example.json") @Bean exampleService () throws Exception{"Creating bean of example json from example.json..." );new ClassPathResource ("example.json" , this .getClass().getClassLoader()).getFile();return new ExampleService (new String (Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(file.toURI()))));
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate
类似 ConditionalOnBean,但要求全局只有一个 bean,或者可以决策出 primary bean 的时候,才会初始化一个 Bean。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Bean @ConditionalOnEnabledInfoContributor("git") @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(GitProperties.class) @ConditionalOnMissingBean @Order(DEFAULT_ORDER) public GitInfoContributor gitInfoContributor (GitProperties gitProperties) {return new GitInfoContributor (gitProperties, this .properties.getGit().getMode());
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
和 @ConditionalOnNotWebApplication 正相反。
1 2 3 4 @ConditionalOnWebApplication healthCheckController () {
@ConditionalOnClass
只有存在一个特定的类的时候,才会初始化一个 Bean。
1 2 3 4 5 @Configuration @ConditionalOnClass(DataSource.class) class MySQLAutoconfiguration {
@ConfigurationProperties
Spring Boot 有个更复杂的属性加载顺序,见《2. Externalized Configuration》 :
Devtools global settings properties in the $HOME/.config/spring-boot folder when devtools is active.
@TestPropertySource annotations on your tests.
properties attribute on your tests. Available on @SpringBootTest and the test annotations for testing a particular slice of your application.
Command line arguments
Properties from SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON (inline JSON embedded in an environment variable or system property).
ServletConfig init parameters.
ServletContext init parameters.
JNDI attributes from java:comp/env.
Java System properties (System.getProperties()).
OS environment variables.
A RandomValuePropertySource that has properties only in random.*.
Profile-specific application properties outside of your packaged jar (application-{profile}.properties and YAML variants).
Profile-specific application properties packaged inside your jar (application-{profile}.properties and YAML variants).
Application properties outside of your packaged jar (application.properties and YAML variants).
Application properties packaged inside your jar (application.properties and YAML variants).
@PropertySource annotations on your @Configuration classes. Please note that such property sources are not added to the Environment until the application context is being refreshed. This is too late to configure certain properties such as logging.* and spring.main.* which are read before refresh begins.
Default properties (specified by setting SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Configuration @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "javadoop.database") public class DataBase {
惰性加载
By default, ApplicationContext implementations eagerly create and
1 2 3 spring: main: lazy-initialization: true
随机值
1 2 3 4 random.number=${random.int} random.long=${random.long} random.uuid=${random.uuid}