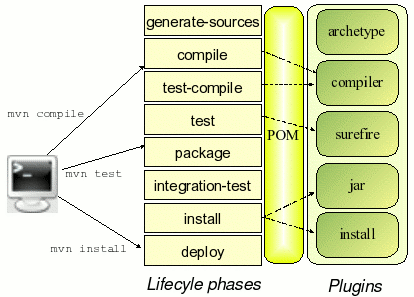
本文主要参考了《Guide to Configuring Plug-ins》:
maven 实际上有两种插件:
- 构建插件,需要在
<build/>元素里配置。如<build><pluginManagement/></build>,当然也有<build><plugins/></build>。
- 报告插件,会在“site generation”里被执行,应该在
<reporting/>里配置。如<reporting><plugins/></reporting>。
要引用插件至少要有三个元素:groupId,artifactId, version。
mojo 是什么
根据《What is MOJO in Maven?》,mojo 是 Maven plain Old Java Object 的意思。实际上是可执行的 goal。
通用配置
一个插件通常包含一个以上的mojo,当一个 mojo 被映射到 goal 的时候,则包含多个 mojo(即一个插件可能有多个 goal)。maven 通过 元素来配置 maven 插件, 的子元素,就会映射到 mojo 的字段,或者 setter 里。
假设有一个mojo:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public class MyQueryMojo
extends AbstractMojo
{
private String url;
private int timeout;
private String[] options;
public void execute()
throws MojoExecutionException
{
...
}
}
|
生成的 xml 就如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| <project>
...
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-myquery-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
<configuration>
<url>http://www.foobar.com/query</url>
<timeout>10</timeout>
<options>
<option>one</option>
<option>two</option>
<option>three</option>
</options>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
...
</project>
|
可以看到<configuration/>确实是 schemaless 的。
而且这些 field 上的注释可以注明缺省值,以及与命令行参数一起使用时的表达式:
1
2
|
mvn myquery:query -Dquery.url=http://maven.apache.org
|
查看帮助
通常插件都带有一个help的 goal,通常可以用以下的方法查看(自行替换插件名称):
1
| mvn javadoc:help -Ddetail -Dgoal=javadoc
|
配置参数
普通类型
基本类型的映射,就使用字面量配置<configuration/>元素:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <configuration>
<myString>a string</myString>
<myBoolean>true</myBoolean>
<myInteger>10</myInteger>
<myDouble>1.0</myDouble>
<myFile>c:\temp</myFile>
<myURL>http://maven.apache.org</myURL>
</configuration>
|
复杂类型
如果有复杂(complex not compoud)类型映射的需要:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <configuration>
<person>
<firstName>Jason</firstName>
<lastName>van Zyl</lastName>
</person>
</configuration>
|
maven 会以大写首字母的方式,在 mojo 本身存在的包里寻找 person 类,否则,就要指定包名:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <configuration>
<person implementation="com.mycompany.mojo.query.SuperPerson">
<firstName>Jason</firstName>
<lastName>van Zyl</lastName>
</person>
</configuration>
|
列表类型
同数组不同,列表类型在 maven 的xml 语法里不是强类型的(换言之,数组是):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class MyAnimalMojo
extends AbstractMojo
{
private List animals;
public void execute()
throws MojoExecutionException
{
...
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| <project>
...
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-myanimal-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
<configuration>
<animals>
<animal>cat</animal>
<animal>dog</animal>
<animal>aardvark</animal>
</animals>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
...
</project>
|
其映射规则是:
- If the XML element contains an implementation hint attribute, that is used
- If the XML tag contains a ., try that as a fully qualified class name
- Try the XML tag (with capitalized first letter) as a class in the same package as the mojo/object being configured
- If the element has no children, assume its type is String. Otherwise, the configuration will fail.
map 类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| ...
<configuration>
<myMap>
<key1>value1</key1>
<key2>value2</key2>
</myMap>
</configuration>
...
|
Properties 类型
和 map 表达嵌套的方式恰好又不一样了,更加工整:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
private Properties myProperties;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <configuration>
<myProperties>
<property>
<name>propertyName1</name>
<value>propertyValue1</value>
<property>
<property>
<name>propertyName2</name>
<value>propertyValue2</value>
<property>
</myProperties>
</configuration>
|
配置构建插件
使用<executions>标签
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| <project>
...
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-myquery-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>execution1</id>
<phase>test</phase>
<configuration>
<url>http://www.foo.com/query</url>
<timeout>10</timeout>
<options>
<option>one</option>
<option>two</option>
<option>three</option>
</options>
</configuration>
<goals>
<goal>query</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>execution2</id>
<configuration>
<url>http://www.bar.com/query</url>
<timeout>15</timeout>
<options>
<option>four</option>
<option>five</option>
<option>six</option>
</options>
</configuration>
<goals>
<goal>query</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
...
</project>
|
注意,在一个 POM 的一个插件里,execution id 必须是唯一的。
一个 plugin 在多个 phase 多次被执行的例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| <project>
...
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
...
<executions>
<execution>
<id>execution1</id>
<phase>test</phase>
...
</execution>
<execution>
<id>execution2</id>
<phase>install</phase>
<configuration>
<url>http://www.bar.com/query</url>
<timeout>15</timeout>
<options>
<option>four</option>
<option>five</option>
<option>six</option>
</options>
</configuration>
<goals>
<goal>query</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
...
</project>
|
下面这个 mojo,用注释标明了这个 plugin/goal 的默认 phase:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public class MyBindedQueryMojo
extends AbstractMojo
{
private String url;
private int timeout;
private String[] options;
public void execute()
throws MojoExecutionException
{
...
}
}
|
我们可以使用 xml 配置来覆盖初始配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| <project>
...
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-myquery-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>execution1</id>
<phase>install</phase>
<configuration>
<url>http://www.bar.com/query</url>
<timeout>15</timeout>
<options>
<option>four</option>
<option>five</option>
<option>six</option>
</options>
</configuration>
<goals>
<goal>query</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
...
</project>
|
曾经,maven 插件的如果处于内部,则无法被命令行 invocation 调用,因为它必须到指定生命周期 phase 才可以被使用。但自 Maven 3.3.1 以后,我们可以直接这样做:
1
2
|
mvn myqyeryplugin:queryMojo@execution1
|
使用<dependencies>标签
插件自己也有自己的默认 dependency,我们可以在插件内部自己使用<dependencies>来更换它的依赖。如 Maven Antrun Plugin version 1.2 使用的 Ant version 1.6.5,我们可以这样更新依赖(兼容性自己保证):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| <project>
...
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-antrun-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
...
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.ant</groupId>
<artifactId>ant</artifactId>
<version>1.7.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.ant</groupId>
<artifactId>ant-launcher</artifactId>
<version>1.7.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
...
</project>
|
在构建插件里使用<inherited>标签
默认的插件配置是会被传播(propagated)到子 pom 里的,所以可以显式地设置<inherited>为 false 来打破这种属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| <project>
...
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-antrun-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
<inherited>false</inherited>
...
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
...
</project>
|
配置 reporting 插件
使用 <reporting> Tag VS <build> Tag
<build> 标签里也可以配置 reporting 插件,但大部分情况下<reporting>里的配置都优先被使用。具体细则见 maven 原文档。
使用<reportSets>标签
如果我们想要选择性地生成报告,我们可以使用<reportSets>标签,只有被它包括的报告,才被选中生成:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| <project>
...
<reporting>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-project-info-reports-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.1.2</version>
<reportSets>
<reportSet>
<reports>
<report>project-team</report>
</reports>
</reportSet>
</reportSets>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</reporting>
...
</project>
|
推而广之,一份报告都不生成的时候,我们可以这样做:
1
2
3
4
5
| <reportSets>
<reportSet>
<reports/>
</reportSet>
</reportSets>
|
在报告插件中使用<inherited>标签
同构建插件差不多
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <project>
...
<reporting>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-project-info-reports-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.1.2</version>
<inherited>false</inherited>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</reporting>
...
</project>
|